Delight your child with a variety of printable prince crowns. Ideal for birthdays, dress-up play, or simple fun at home, these crowns can help create joyful, imaginative play for your child while making them feel like royalty.
Enhance your classroom with printable prince crowns.
These crowns offer unique learning opportunities for various activities and events and can boost student engagement by contributing to a fun, vibrant learning environment.




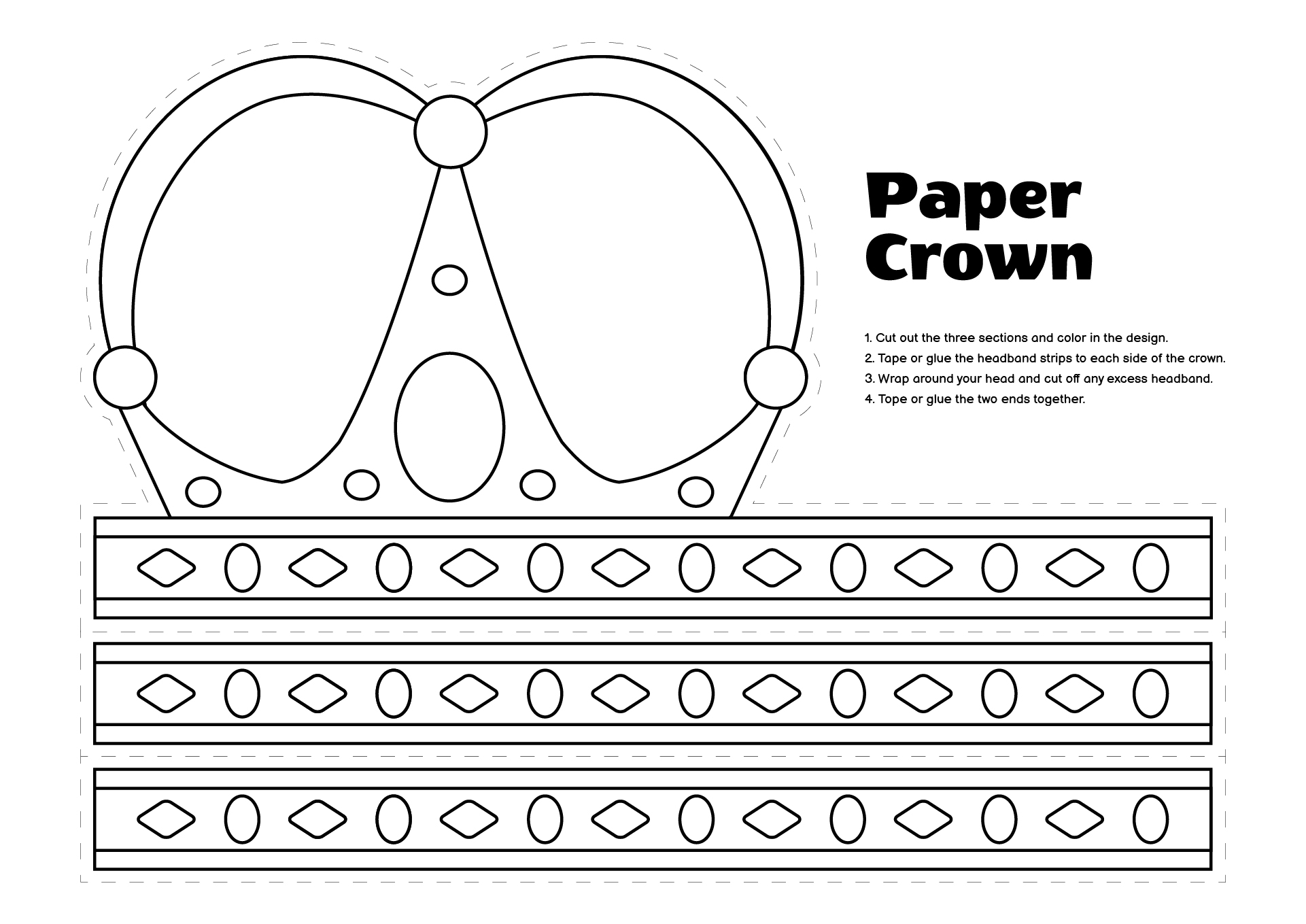
Create your own crown masterpieces with printable prince crown templates. Suitable for prince-themed parties or crafting projects, these crowns can add a regal touch to your creations easily and effectively.
Printable prince crowns can be a fun and stimulating activity for preschool students. Easy-to-assemble, customizable, and promoting imaginative play, these crowns are a handy tool for busy teachers aiming to enhance their students' learning experience.
Prince Crowns Printable refers to printable templates or designs of crowns that can be used for various purposes, such as parties, dress-up activities, or craft projects. You can find a variety of printable prince crown templates that can be downloaded, printed, and then assembled using scissors and glue. These printables are especially useful for kids' birthday parties or themed events where children can have fun creating and wearing their own prince crowns.
Have something to tell us?
Recent Comments
I love the Prince Crowns Printable! It's a simple and charming resource that adds a touch of creativity and imagination to any celebration. Thank you for making this available!
The printable prince crowns allow children to immerse themselves in imaginative play, enhancing their creativity and fostering storytelling skills. Additionally, they serve as a cost-effective solution for themed parties or events, providing a delightful and personalized touch to celebrate with.
Printable prince crown images make it convenient for children to have a royal experience during playtime or parties without the hassle of purchasing physical crowns.