Looking for a periodic table to print out. One that shows atomic mass would be real helpful. Helps in studying and doing homework. Kinda hard to find a clear one that's got everything we need.
We put together a printable periodic table that includes each element's atomic mass. It's designed so you can easily spot the mass numbers and understand the elements better. Handy for students, teachers, or anyone interested in chemistry. Useful for quick reference or study sessions, making learning or teaching about elements more straightforward.

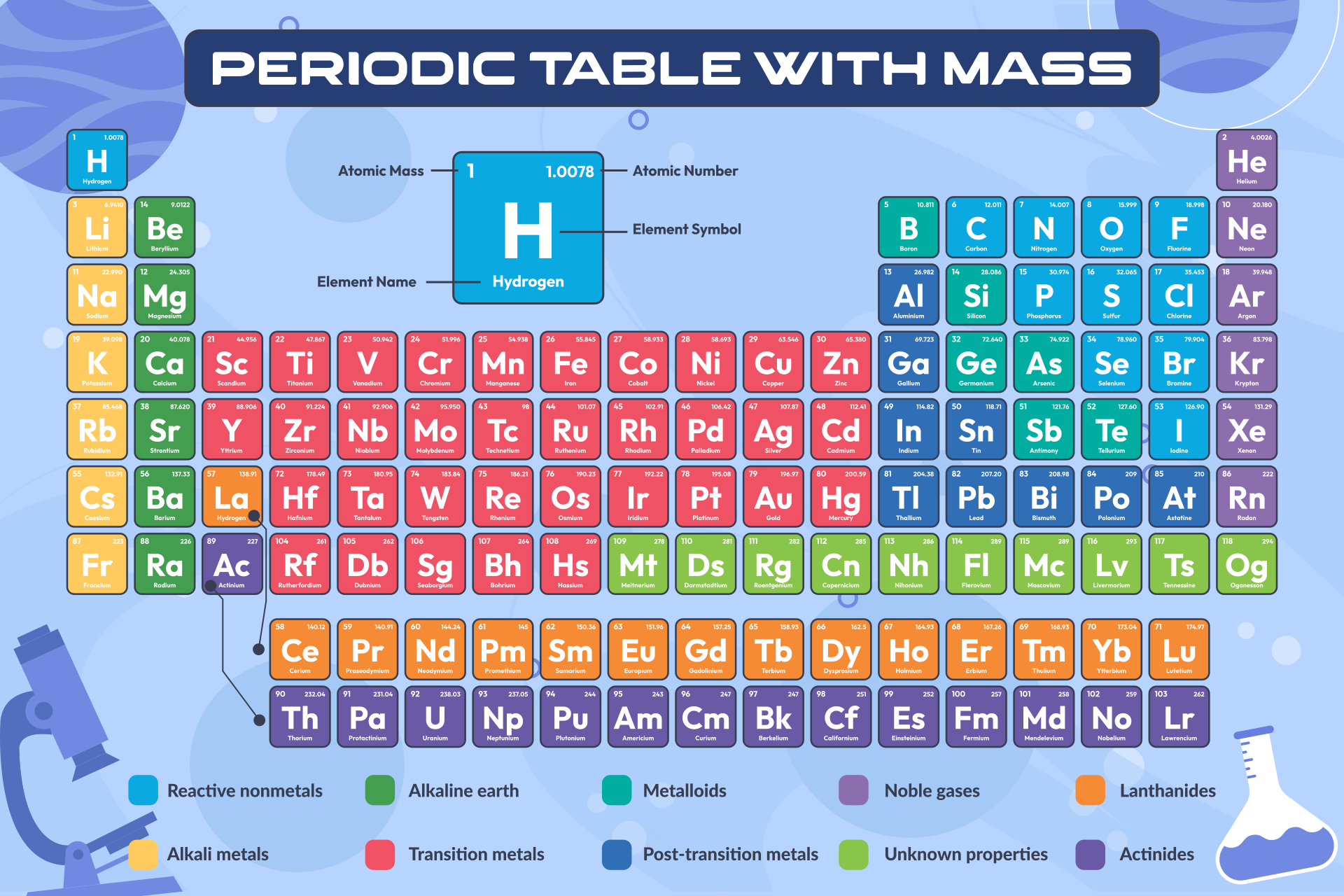
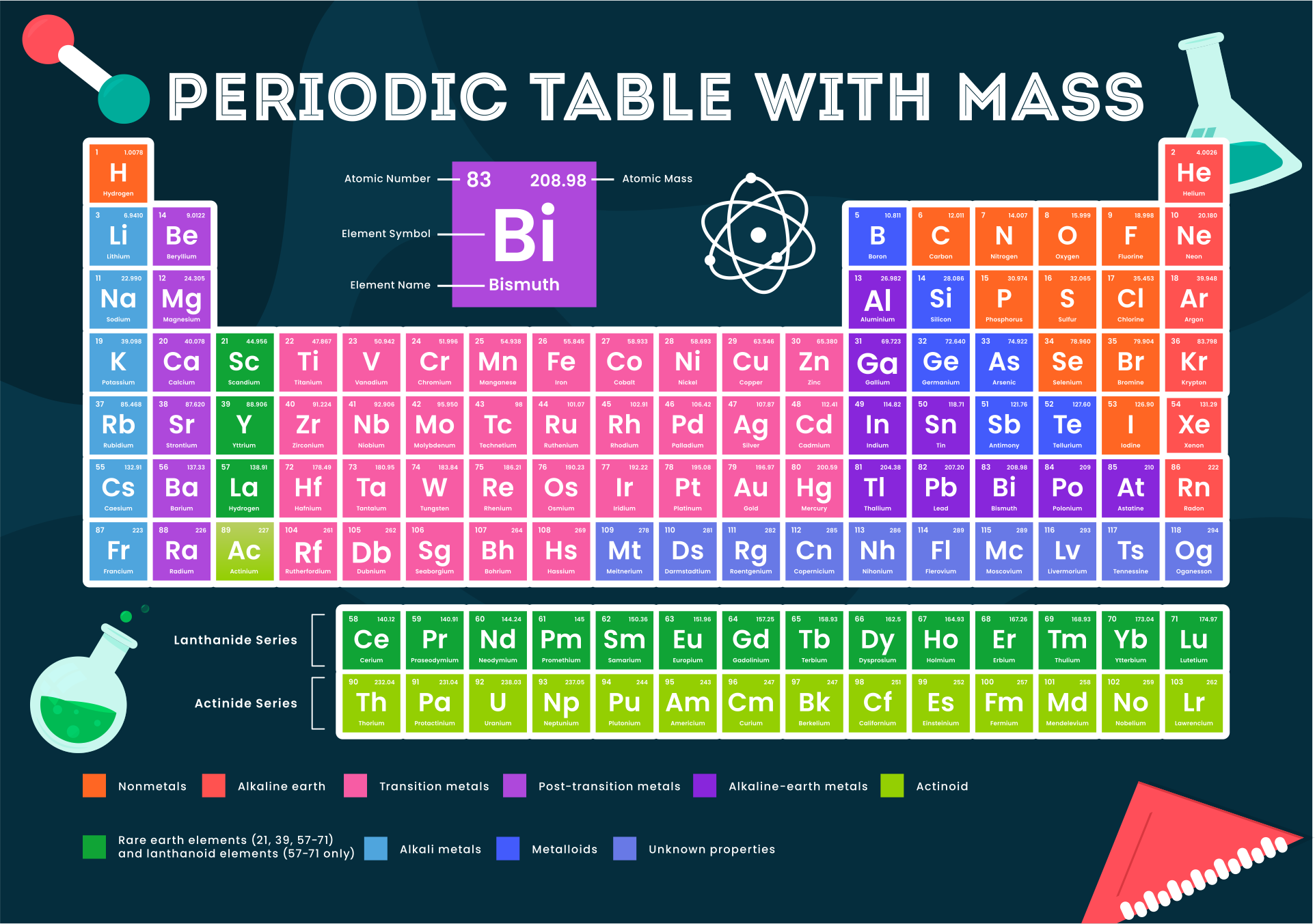
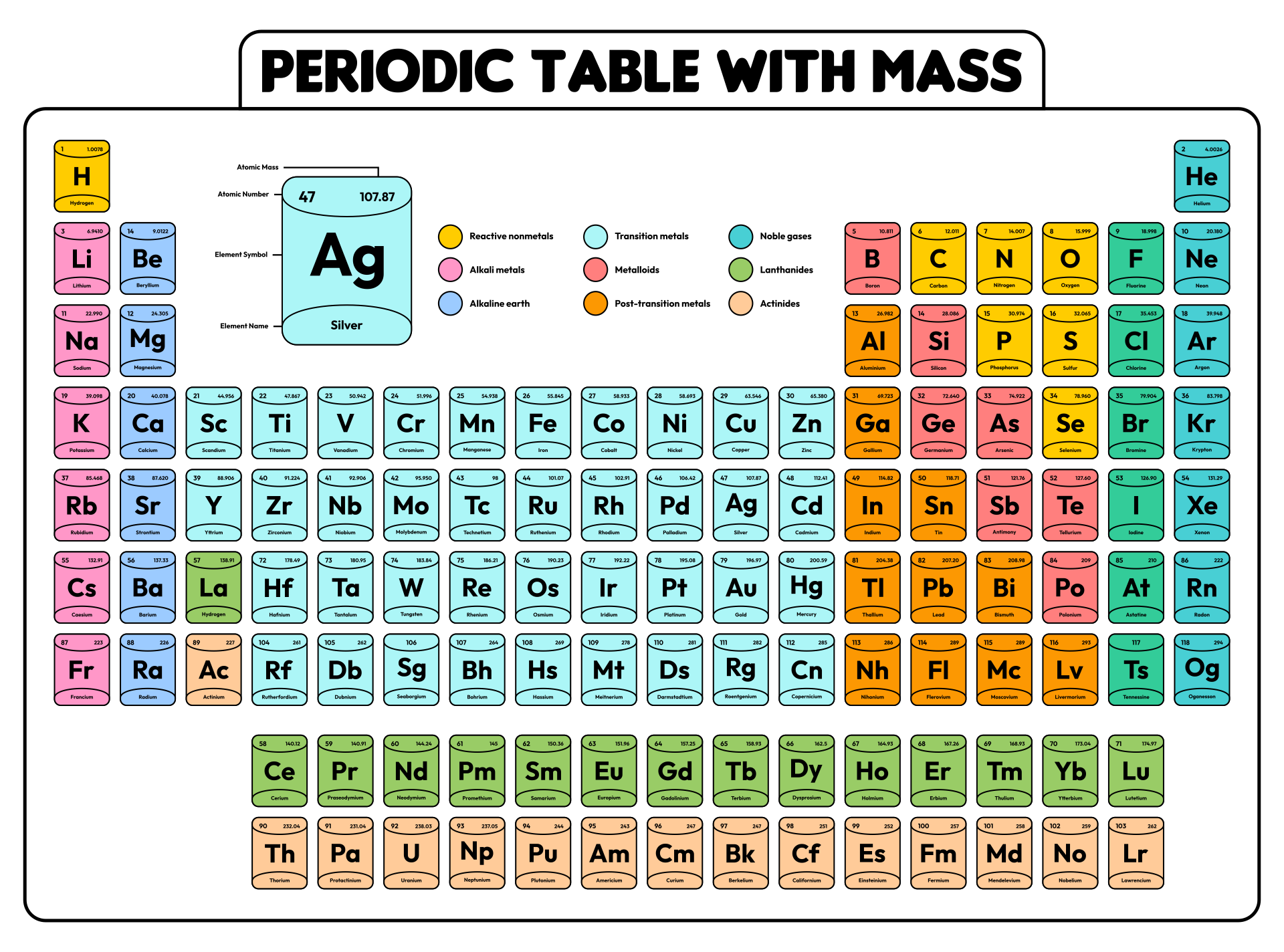
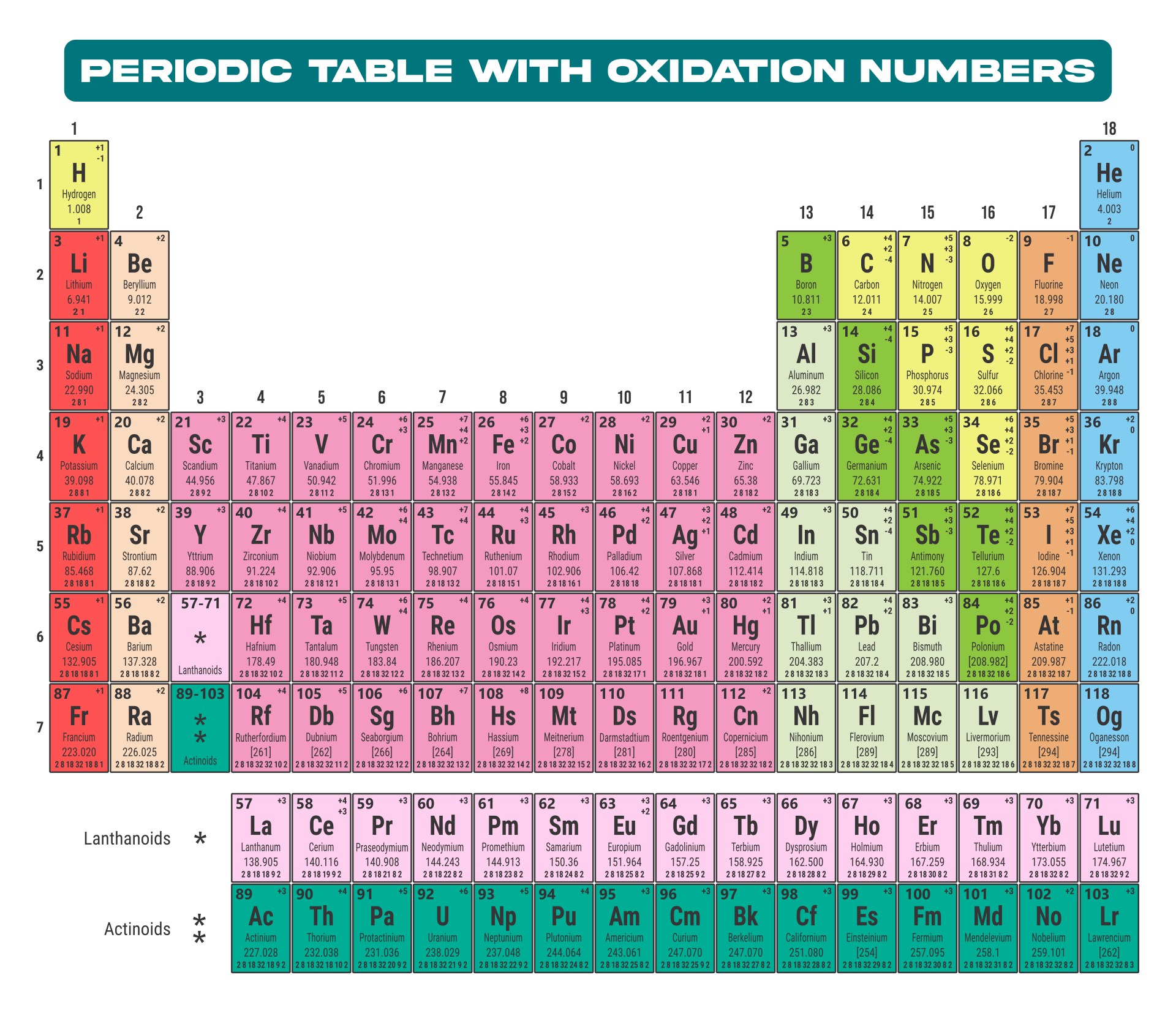
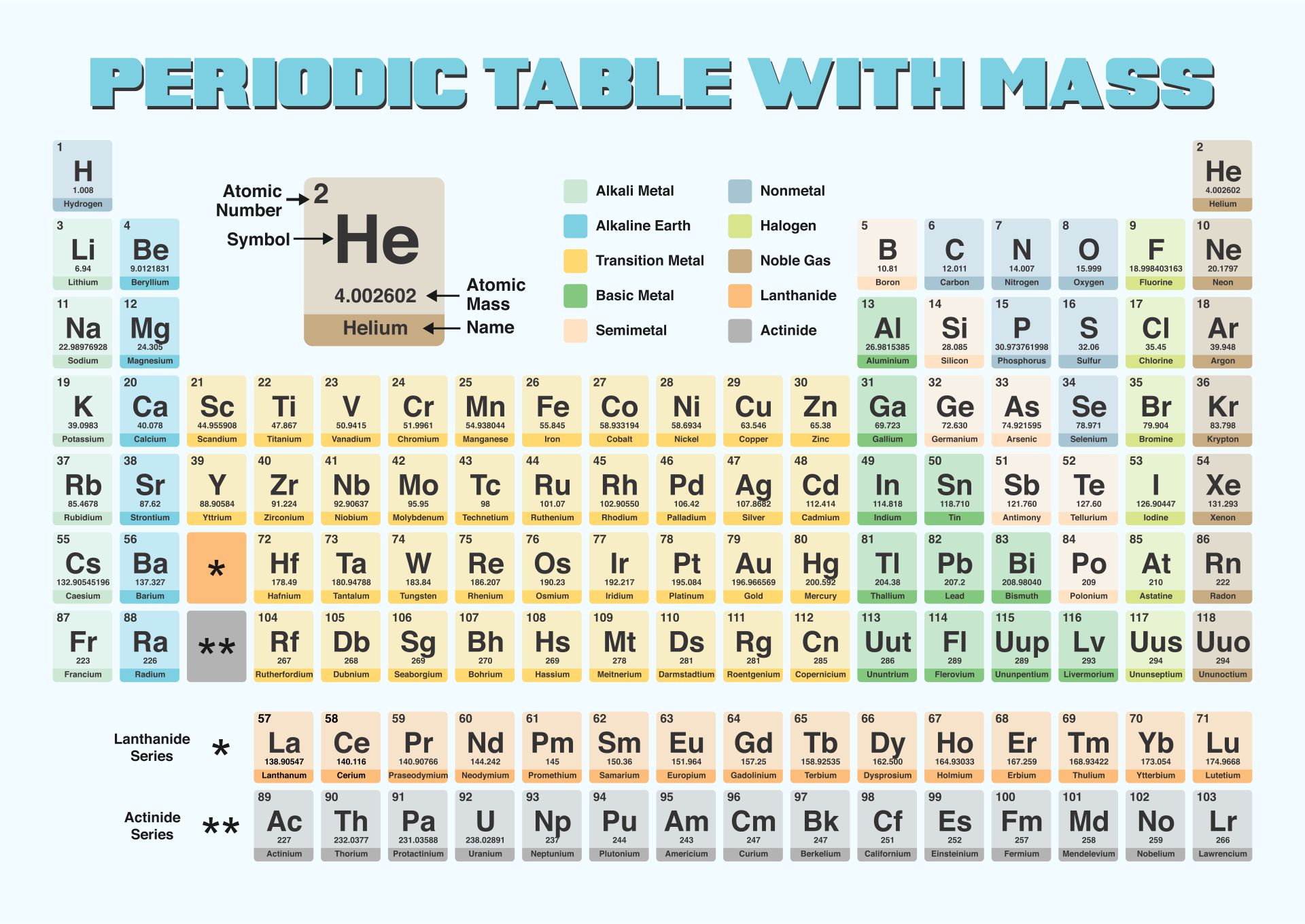
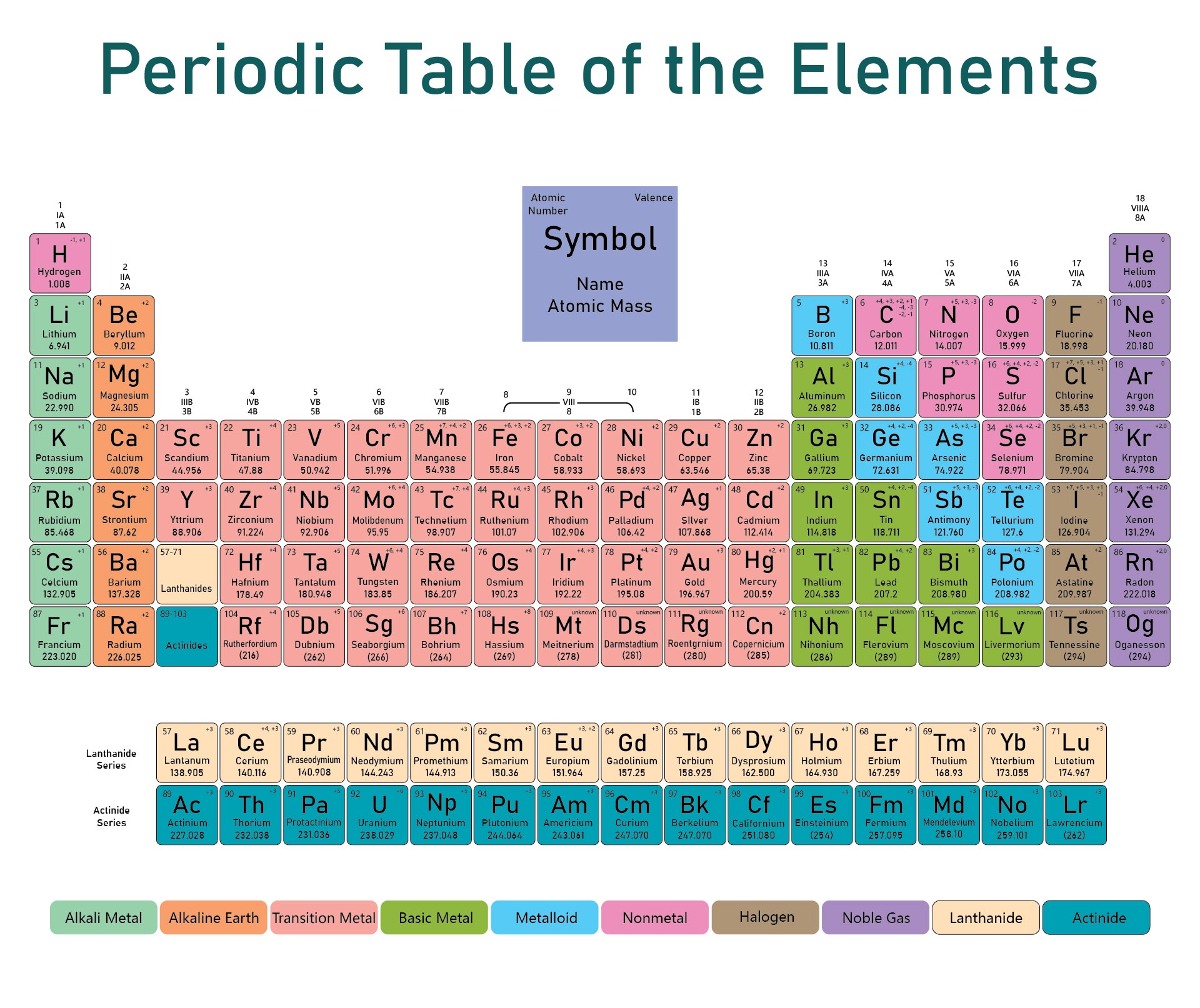
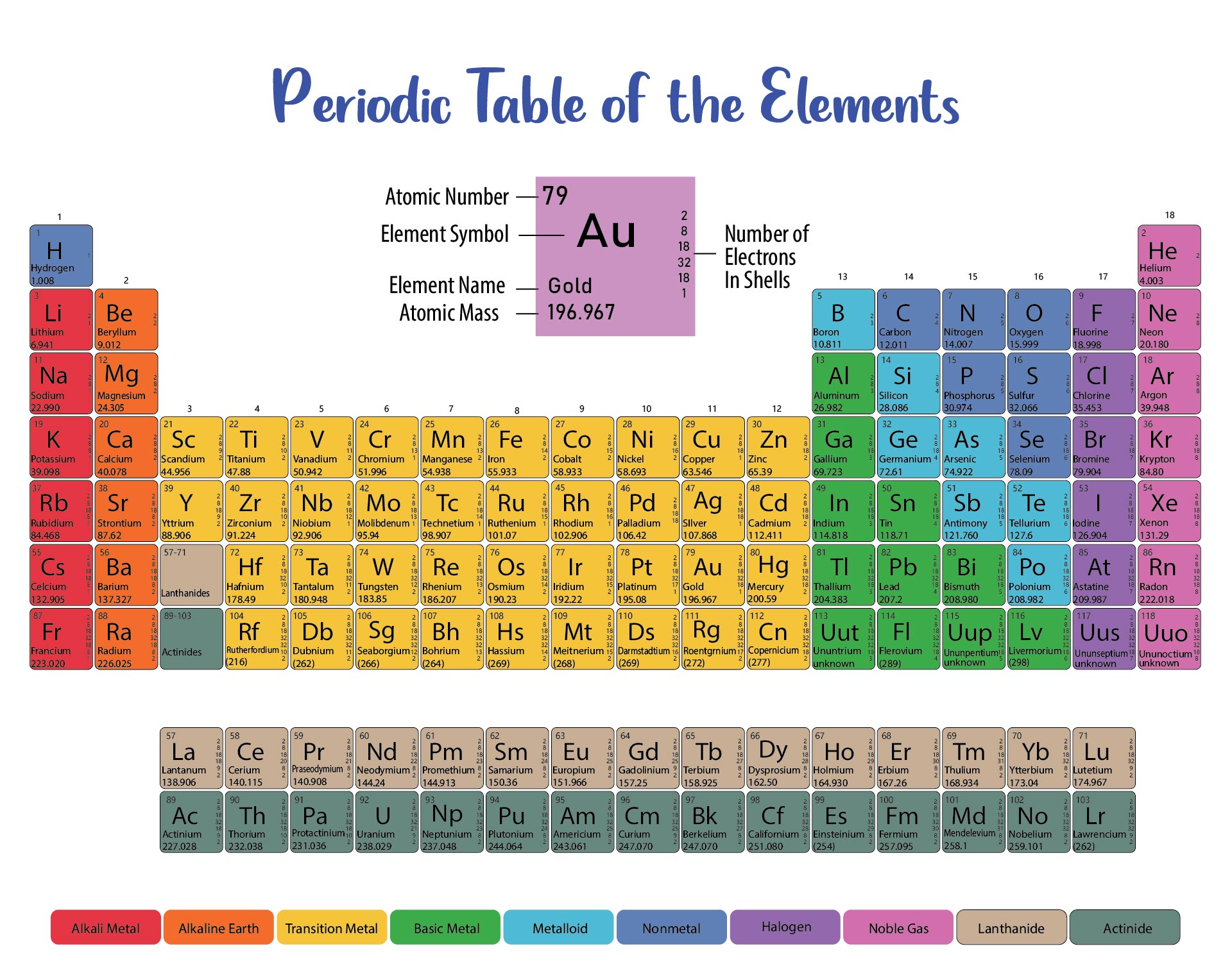
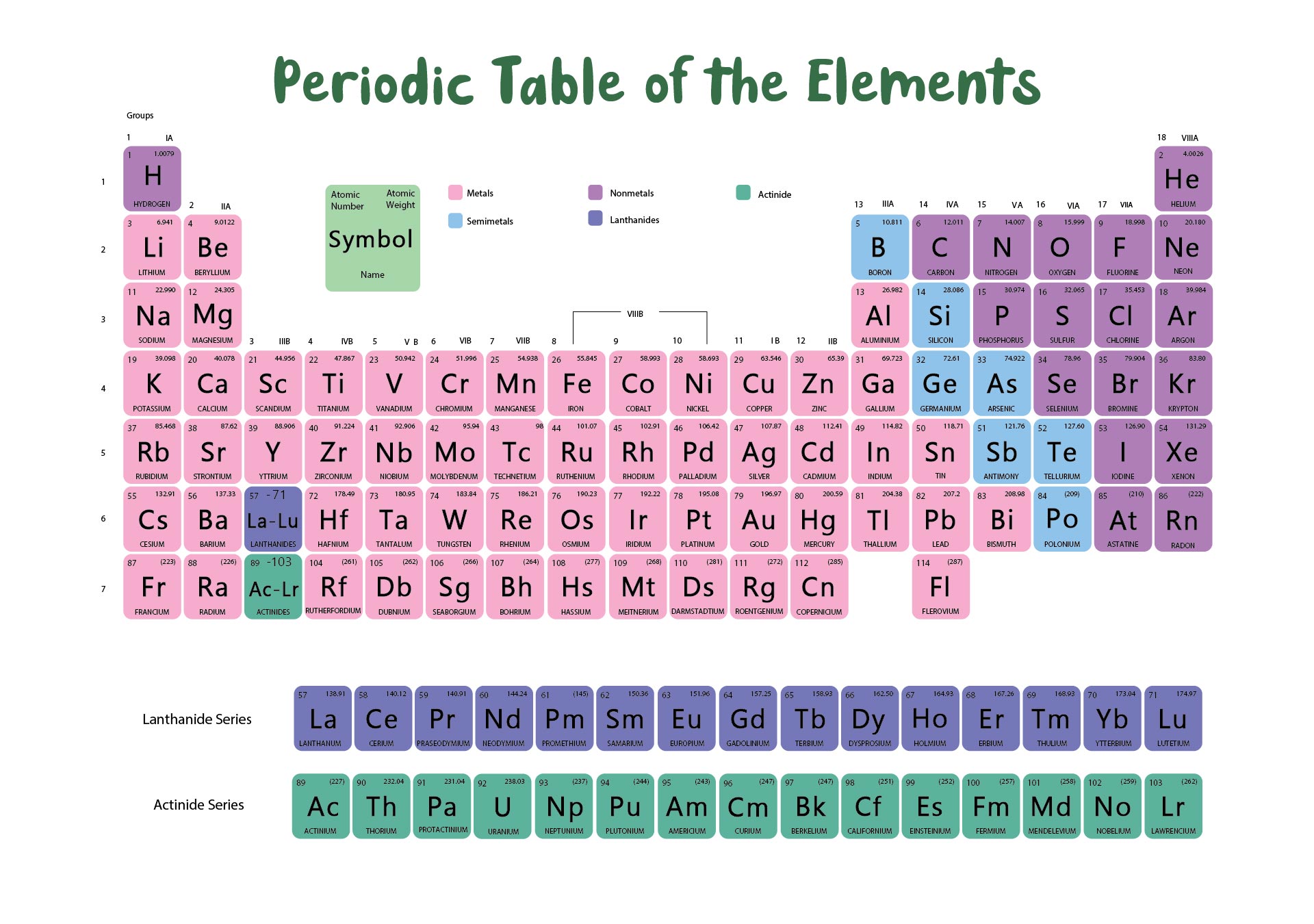
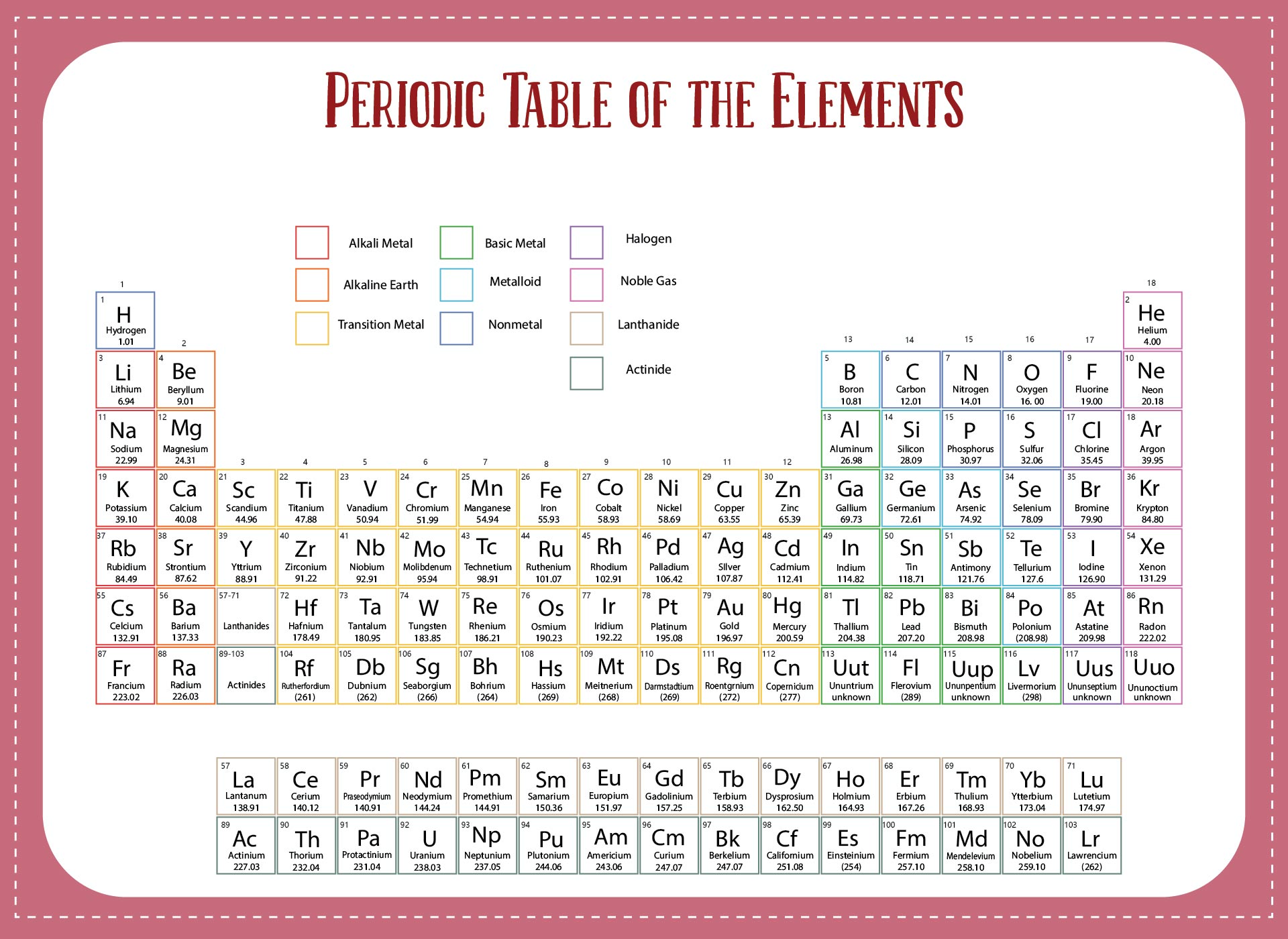
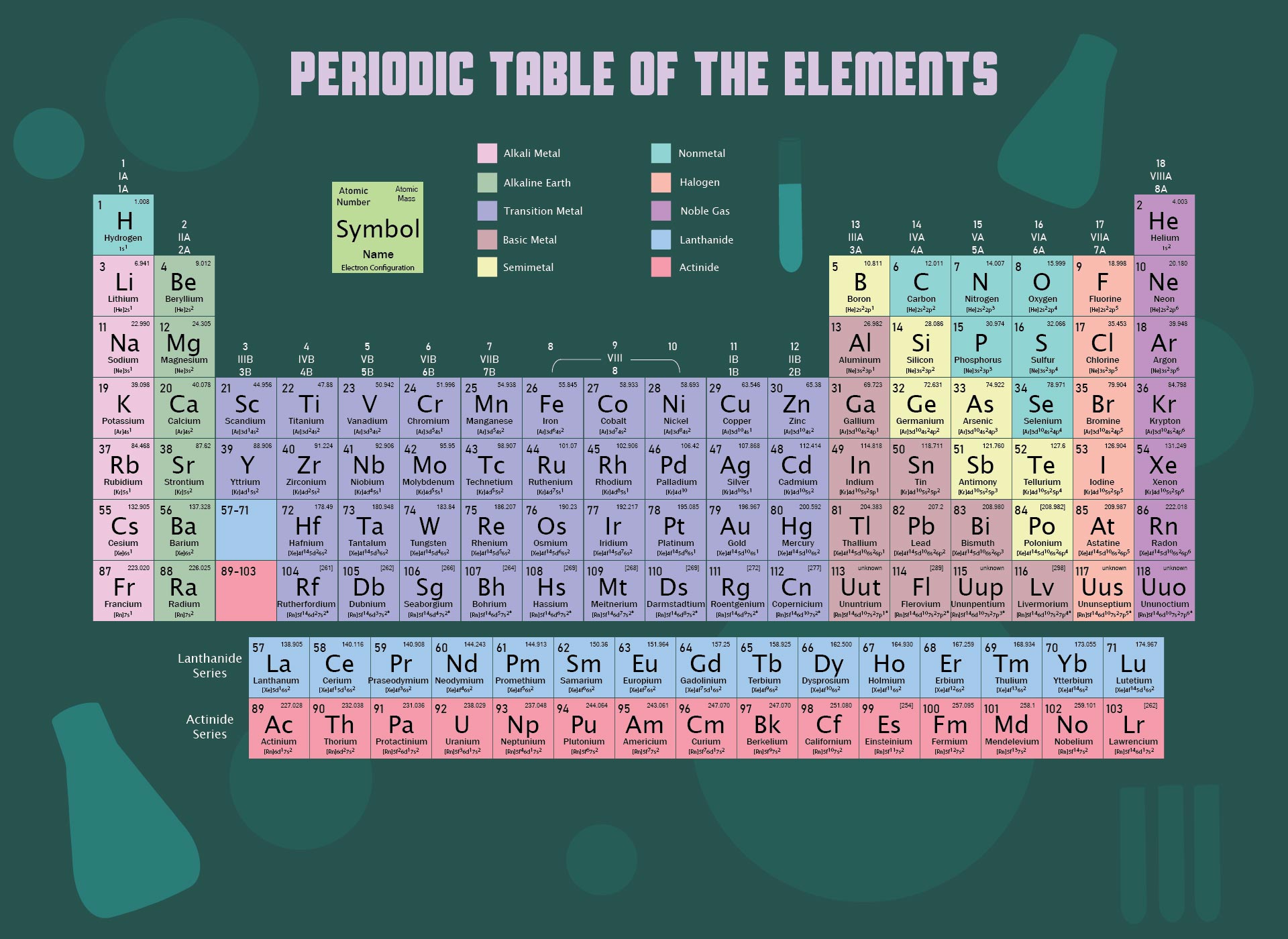
The atomic number, represented by Z, indicates the count of protons in an atom and is crucial in identifying an element. On the other hand, the mass number (or atomic mass), represented by A, accounts for both protons and neutrons, hence giving an element's approximate weight. While atomic number stays constant for a given element, mass number can vary due to different isotopes.
Generally, the atomic number is located next to an element's name on the periodic table, while isotopes of the same element are often distinguished by their atomic masses.
Understanding this distinction is key to a clearer grasp of atomic structure and proper usage of terminologies in chemistry.
Have something to tell us?
Recent Comments
A printable periodic table with mass enables individuals to easily access and study the elements' atomic mass values, aiding in accurate calculations and scientific research.
A printable periodic table with mass allows individuals to conveniently access essential information about the elements, aiding in scientific analysis and research.
This printable periodic table with mass offers a convenient and visually engaging tool for students and professionals alike, enabling easy access to accurate atomic mass values and enhancing the understanding of chemical elements.