A barn template printable can significantly ease your crafting or educational projects by providing a ready-to-use outline that you can customize.
You can effortlessly create themed decorations, develop educational materials for children, or even use it as a planning tool for actual barn projects. Its versatility allows you to scale the design to fit your needs, facilitating activities that range from simple coloring tasks for young learners to more complex model-building exercises.
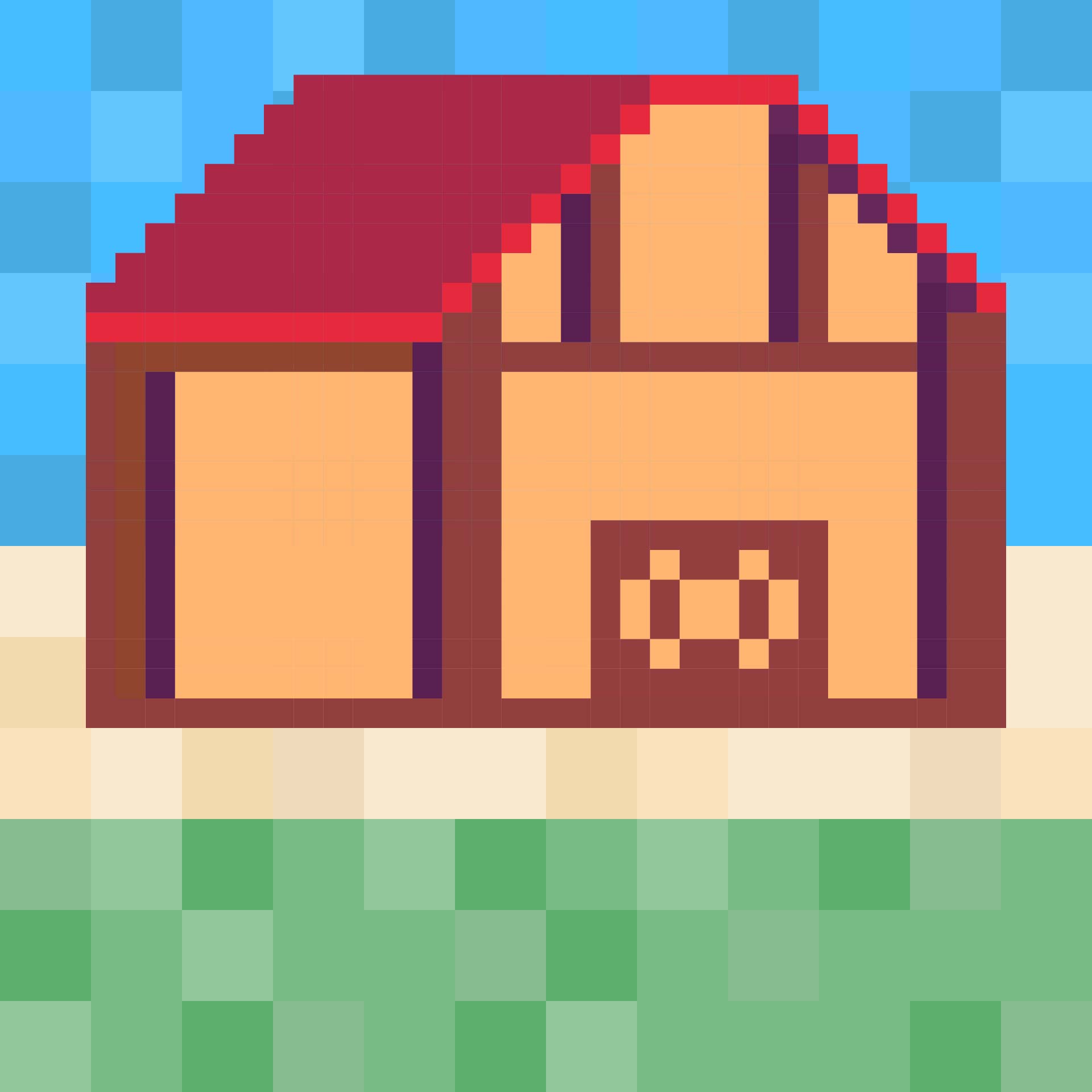


Printable barn templates simplify your crafting and decorating projects, allowing you to create accurate models or thematic decorations for events like farm-themed parties. Perfect for educators and parents, these templates can be a fun and educational tool to teach children about farm life, enhancing their creativity and understanding of rural environments.
Barn applique quilt patterns offer a charming and rustic touch to your quilting projects, turning ordinary blankets into warm, countryside-inspired creations. Ideal for those who enjoy sewing or are looking for a cozy project, these patterns can also make heartfelt gifts or beautiful additions to your home decor.
Engaging in printable barn craft activities can be a delightful way to spend time with your children or students, fostering their creativity while introducing them to agrarian architecture. These crafts serve not only as entertaining educational tools but also help in developing fine motor skills and an appreciation for handmade projects.
A printable barn template can serve as a fantastic tool for various projects, such as craft activities, educational lessons on farm life, or even as a base for creating decorations for a farm-themed party. You can easily customize these templates to fit the needs of your project, adding colors, textures, or additional elements like animals. It's a simple way to bring a touch of the rustic charm of the countryside into your crafts or teaching materials, making learning or decorating more engaging and enjoyable.
Have something to tell us?
Recent Comments
The barn template printable is a useful tool for creating arts, crafts, or educational projects, providing a ready-to-use outline that makes it easy to bring the charm of a barn to life with minimal effort.
A barn template printable offers a convenient and creative way to decorate or educate, allowing you to easily create stunning barn-themed crafts or teaching materials.
The barn template printable is a helpful tool for crafts and educational activities, allowing users to easily create and customize their own barn-themed projects.